




 Heart Arrythmias and Palpitations Natural Recovery from PVCs Premature Ventricular Contractions and Atrial Fibrillation AFib >>
Heart Arrythmias and Palpitations Natural Recovery from PVCs Premature Ventricular Contractions and Atrial Fibrillation AFib >>
Atrial Fibrillation …Embolus…Pulmonary Hypertension…Obstructive Sleep Apnea … PFO Patent Foramen Ovale 1/4 people have it !
ResMed 9 with BiPAP Full Face Quattro Mask with repeat sleep study in lab and home oximetry monitoring every three months – Must us this therapy to control Pulmonary Hypertension
Protocols for Atrial Fibrillation
CORE >>
KardioVasc
Full Vitamin K2
SuperNOX NO2 with Beets
Magnesium Glycinate
Ultra Thimine B1
Gamma E PLUS
Forskolin
Omega Supreme PRO
Ellagic Acid
Nattokinase
CoQ10 Supreme
CoQ10 Supreme Ubiquinol
VascuCare
ADVANCED >>
Power C PLUS
BioLVR
Power Methyl B12
Super Folate

Fusion Beats Are:
- PVCs that occur at the same time as ventricular activation by the underlying rhythm which can cause ventricular depolarization to occur simultaneously in two directions
- This fusion beat results in a QRS complex that has the characteristics of the PVC and the QRS complex of the underlying rhythm


PAC: Premature Atrial Contraction
Definition: A PAC is an ectopic premature beat, not originating from a SA node. The atria are usually irritable in this situation. This irritability is what causes the premature firing of the atrial complex. The ventricular complex is normal. Possible causes are drug interaction, caffeine, fatigue, cardiac ischemia, atrial enlargement, alcohol, anterior myocardial infarction, emotional stress and tobacco. See http://www.mei.com/resource/arrythm/show.cgi?121
EKG Characteristics. Rate: Atrial and ventricular usually normal. Rhythm: Irregular. P Wave: Ectopic P Wave. PR Interval: Usually normal, but could also be greater than 020 seconds. QRS Complex: normal configuration. ST Segment: Normal configuration. T Wave: Usually normal, but could have P Wave hidden in it, which distorts T Waves.
Nursing Intervention: No nursing intervention is needed unless it is a frequent arrhythmia, or it is anew patient. Determine the underlying causes and treat.
PJC: Premature Junctional Complexes
Definition: PJC have an ectopic foci in the AV junctional tissue that paces the heart. The result is a PJC. The P wave may be inverted in lead II as a result of the abnormal conductive pathway. Possible causes are ischemia, hypoxemia, valvular disease, stimulants (caffeine), alcohol, atrial enlargement, emotional stress, digitis toxidity, and it may be a normal variant.
EKG Characteristics: Usually 60-100 beats per minute. Rhythm: Irregular, due to PJC. P Wave: Can occur before, during, or after QRS complex. The P wave also can be inverted in lead II. PR Interval: Less than 0.12 seconds. QRS Complex: Normal in configuration and duration. The QRS complex just occurs sooner due to the PJC. ST Segment: Could be distorted if the P wave follows QTS complex.
Nursing Interventions: No nursing intervention is needed unless the PJCs frequently occur, or if the arrhythmia is new for the patient. Determine the cause and treat the underlying etiology.
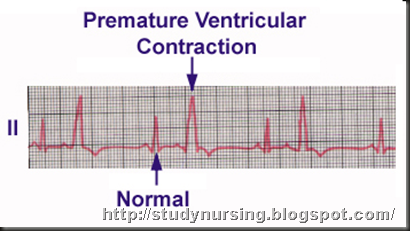
PVC: Premature Ventricular Contractions
Definition: A PVC is an ectopic foci originating in the ventricles. This depolarization is premature. The two ventricles do not usually depolarize simultaneous. A widened QRS complex may result. Three or more PVCs in a row or PVCs lasting more than 30 seconds are considered a run of ventricular tachycardia (VT). PVCs may occur in an isolated complex, or in every other beat (bigeminy), or even in every third beat (trigeneminy). PVC can be isolated incidents without symptoms, which is no cause for alarm, or PVCs can be symptomatic. Possible causes are electolyte imbalances, hypoxia, ischemia, acute myocardial infarction and medical toxicity.
EKG Characteristics: Rate: Normal for the intrinsic rhythm. Rhythm: Regular, except for the PVC. P Wave: None. PR Interval: None. QRS Complex: Greater than 0.12 seconds.
Nursing Intervention: Treatment is only indicated if PVC is symptomatic. Determine the cause of the PVCs and treat the cause. Oxygen administration, standing protocol orders, and notify the MD if this is a new event.
Disclaimer: These Wellness Protocols are not intended to replace the attention or advice of a physician or other qualified healthcare professional. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
